[Java] Thread 이해하기
이 글에서는 Thread 클래스는 'Thread', 개념적 의미의 스레드는 '스레드'로 표기한다.
먼저 프로세스와 스레드의 차이에 대해 잘 모르는 사람들은 이 글을 읽기 바란다.
[OS] 프로세스와 스레드
프로그램 어떤 작업을 위해 실행할 수 있는 파일 메모리에 올라가지 않은 Windows의 *.exe 같은 정적 파일 (메모리에 올라가다: 실행을 하려면 OS가 독립적인 메모리 공간을 할당해줘야 함) 프로세스
yeonyeon.tistory.com
스레드를 생성하는 방법으로는 두 가지가 있다.
- implements Runnable
- extends Thread
🔻 Runnable vs Thread
어느 것을 이용해 스레드를 생성하는 것이 좋을까? 어느 쪽이든간에 별 차이는 없지만 Thread 클래스를 상속받으면 다른 클래스를 상속받을 수 없기 때문에 Runnable 인터페이스를 구현하는 방법이 일반적이다.
➕ 인터페이스의 장점: https://yeonyeon.tistory.com/208
[Java] 인터페이스를 사용하자!
자바는 다중 구현을 위해 인터페이스, 추상 클래스 기능을 제공한다. 그러면 어느 것을 사용하는게 더 좋을지 한번 고민해보자! 🤗 인터페이스의 장점 ❗ 자유로운 추가 자바는 단일 상속
yeonyeon.tistory.com
✨ Runnable
- 스레드를 생성하는 모든 클래스는 Runnable 구현이 필수적
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Runnable {
public abstract void run();
}
🌠 run()
When an object implementing interface Runnable is used to create a thread, starting the thread causes the object's run method to be called in that separately executing thread.
ㅡ Oracle Docs
스레드 생성을 위해 Runnable 인터페이스를 구현하는 객체를 만들어보자. 생성된 스레드를 시작하면 기존에 실행 중이던 스레드에서 run 메서드가 호출된다. 예제 코드를 통해 확인해보자.
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread thread = new Thread(new RunnableThread());
System.out.println("before start: " + Thread.currentThread());
thread.start(); // 스레드 실행
System.out.println("after start: " + Thread.currentThread());
System.out.println("before join: " + Thread.currentThread());
thread.join(); // thread 작업 끝날 때까지 메인 스레드 일시정지
System.out.println("after join: " + Thread.currentThread());
}
private static final class RunnableThread implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("run method: " + Thread.currentThread());
}
}
}
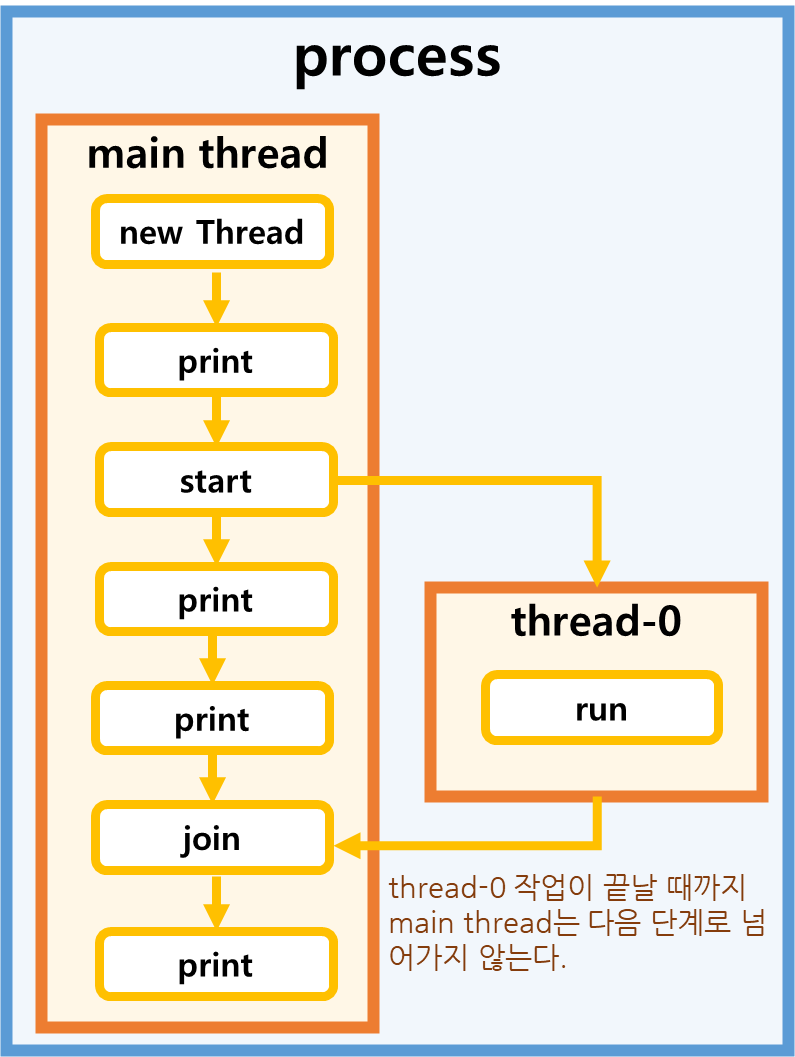
🔻 왜 start() 메서드가 아닌 join() 메서드 호출 후에 프린트 될까?
먼저 동시성과 병렬성이란 단어의 차이를 인지해야 한다.
- 동시성; Concurrency
: 동시 실행되는 것처럼 보임 - 병렬성; Parallelism
: 실제로 동시에 실행
더 자세히 보기 👉 https://yeonyeon.tistory.com/270
동시성 (Concurrency) vs 병렬성 (Parallelism)
😎 서론 이전 포스팅에서 동시성과 병렬성 차이에 대해서 아래처럼 간략하게 서술했었다. 동시성: 하나의 코어에서 여러 스레드가 번갈아가며 실행 병렬성: 멀티 코어에서 여러 스레드를 동시
yeonyeon.tistory.com
run() 메서드가 join() 메서드보다 나중에 실행된 것처럼 보이는 이유는 스레드가 병렬로 실행되고 있기 때문이다. 위 예제의 결과 화면을 보면 main 스레드와 Thread-0 스레드의 존재를 확인할 수 있다. 이 스레드들은 병렬로 실행되고 있다. main 메서드의 중간에서 호출하는 join() 메서드는 Thread-0 스레드의 작업이 종료될 때까지 main 스레드를 일시중지 시킨다. Thread-0의 모든 작업(예제코드로 따지면 run() 메서드 실행하기)이 끝나고나서야 "after join: ~~"를 출력하는 Main 스레드의 작업을 실행할 수 있게 된다.
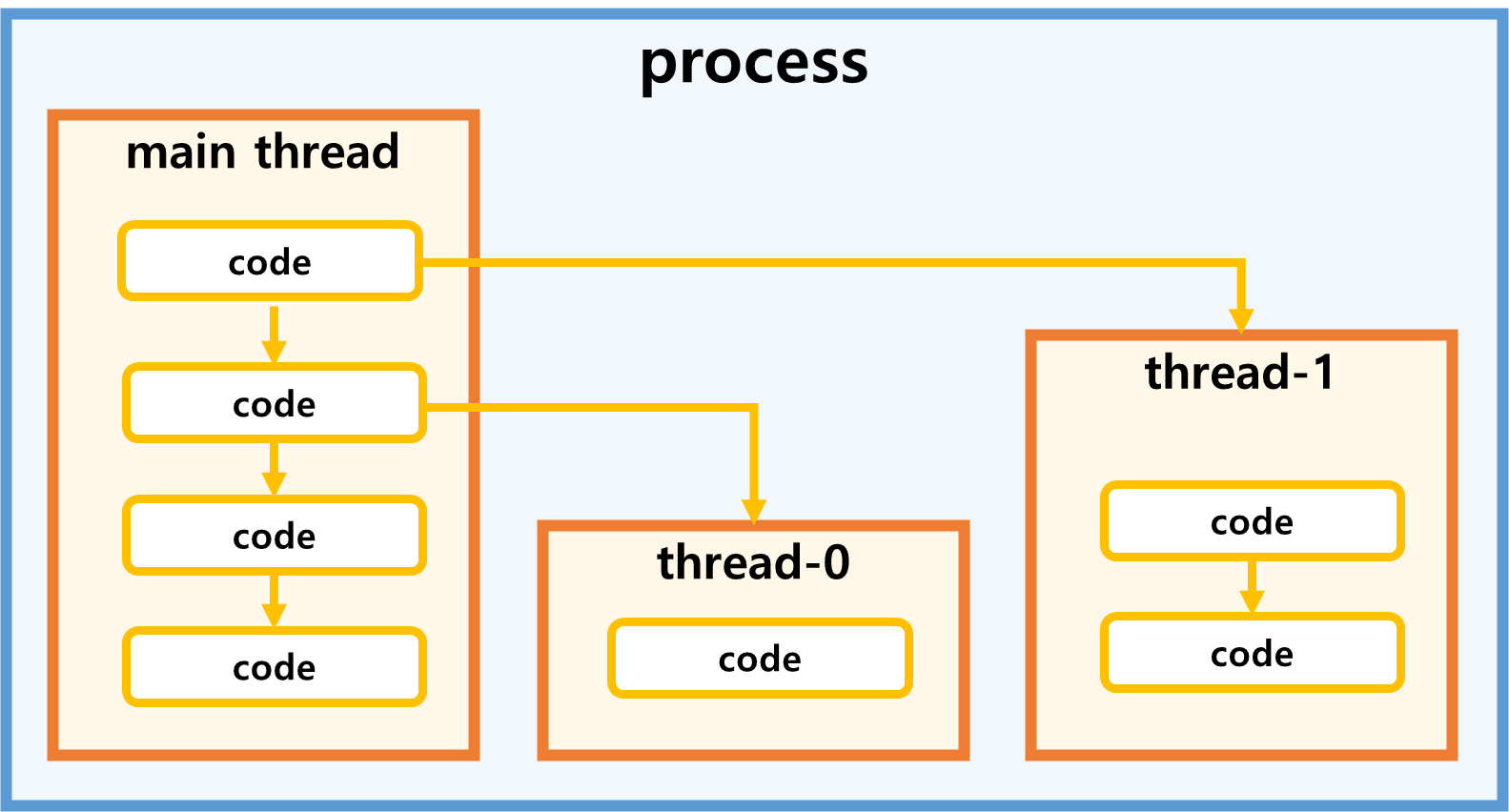
✨ Thread
- 스레드를 생성하는 또다른 방법
- Thread 클래스는 Runnable을 구현
public class Thread implements Runnable { ... }
🌠 스레드 상태
Thread와 관련된 메서드들을 소개하기 앞서 스레드의 상태에 대해서 알아보자. 스레드 상태 종류는 아래와 같다. 노란 동그라미 안에 있는 글씨는 스레드 상태의 한글/영문 표기이고 갈색 글씨로 쓰여있는 start(), notify() 등은 Thread 클래스의 메서드명이다.
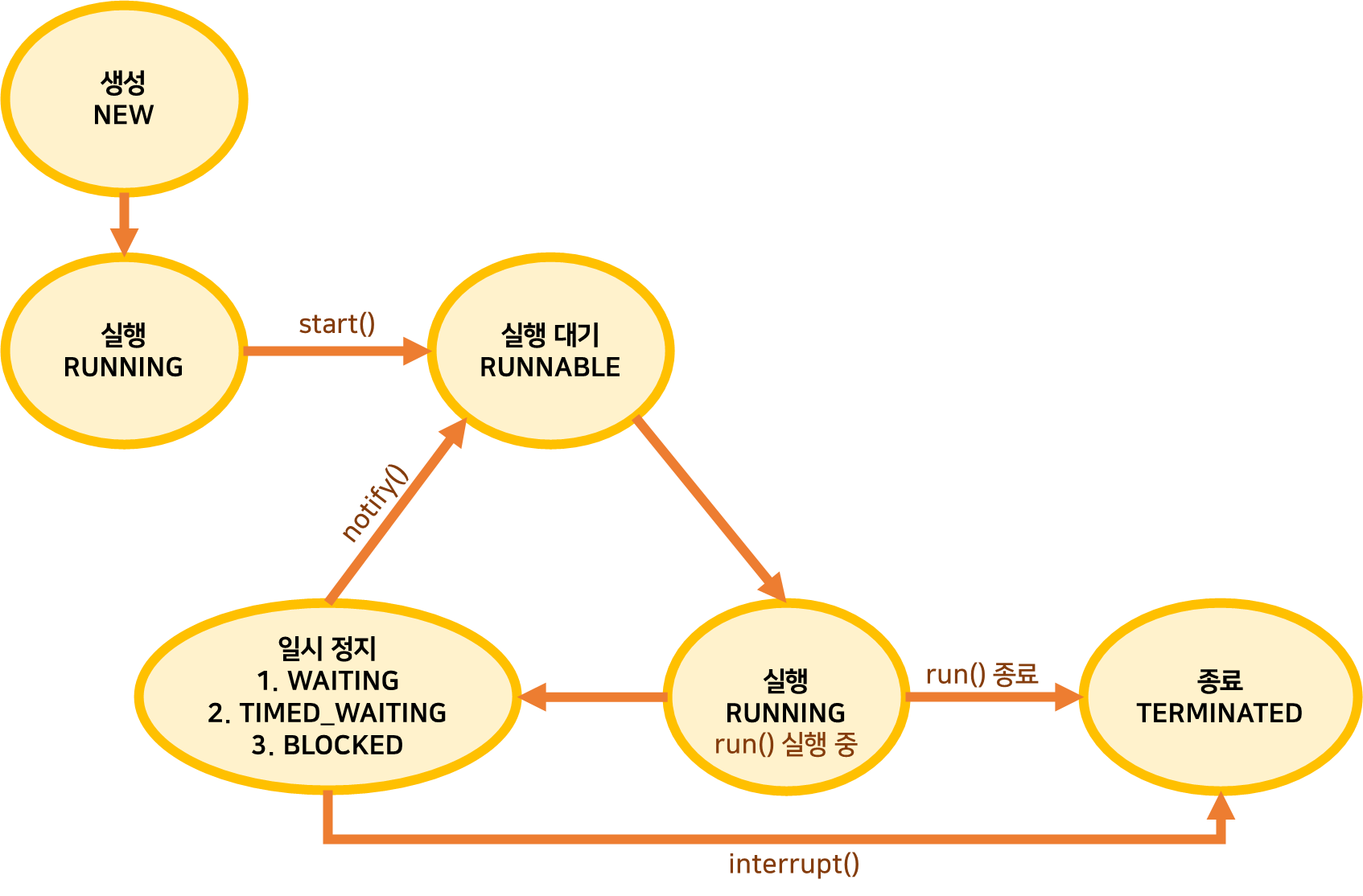
다른 상태들과는 달리 일시 정지에는 여러 종류가 존재한다.
- WAITING: 다른 스레드가 통지할 때까지 기다리는 상태
- TIMED_WAITING: 주어진 시간 동안 기다리는 상태
- BLOCKED: 사용하려는 객체의 락이 풀릴 때까지 기다리는 상태
🌠 start()
- 스레드를 실행 대기 상태로 만듦
- 실행대기 상태에 있다가 자신의 차례가 오면 실행
(실행 순서는 OS의 스케쥴러가 작성한 스케쥴에 의해 결정) - Thread는 단 한번의 start()만 가능
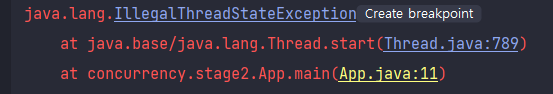
🔻 Thread 여러번 start하기
스레드를 여러번 시작하면 IllegalThreadStateException이 발생한다.
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
Thread thread = new ExtendsThread();
thread.start();
thread.start();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
여러번 start()를 호출하고 싶다면 새로운 스레드를 생성해야 한다.
(새로운 스레드를 생성한거니 사실상 한 스레드를 여러번 start하는 방법은 없다..)
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
Thread thread = new ExtendsThread();
thread.start();
thread = new ExtendsThread();
thread.start();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
🌠 interrupt()
- 일시 정지 상태의 스레드에서 InterruptedException 예외 발생
- 예외 처리 코드(catch)에서 실행 대기 상태 도는 종료 상태로 갈 수 있게 함
- 유사한 메서드로는 stop() 메서드가 있음 (Deprecated)
🔻 interrupt 예제
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread());
Thread thread = new Thread(new RunnableThread());
thread.start();
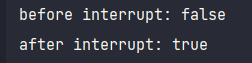
System.out.println("before interrupt: " + thread.isInterrupted());
thread.interrupt();
System.out.println("after interrupt: " + thread.isInterrupted());
}
private static class RunnableThread implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
}
}
}
🌠 wait(), notify(), notifyAll()
- Thread 클래스에서 생성한 메서드가 아닌 Object 클래스의 메서드
- wait()
- : synchronized 블록 내에서 스레드를 일시 정지 상태로 만듦
- wait(long millis) 등을 통해 시간을 주면 해당 시간 동안만 일시 정지로 만듦
- 유사한 메서드로는 Thread의 suspend()가 있음 (Deprecated)
- notify(), notifyAll()
- : wait() 메서드에 의해 일시 정지 상태에 있는 스레드를 실행 대기 상태로 변경
- 유사한 메서드로는 Thread의 resume()가 있음 (Deprecated)
🌠 sleep()
- 주어진 시간 동안 스레드를 일시 정지 상태로 만듦
🌠 join()
- 다른 스레드의 종료 대기
- join() 메서드를 호출한 스레드를 일시 정지로 전환
- join() 메서드를 멤버로 갖는 스레드가 종료되거나 매개값으로 주어진 시간이 지나면 실행 대기 상태가 됨
- 예제는 상단의 '왜 start() 메서드가 아닌 join() 메서드 호출 후에 프린트 될까?' 참고
🌠 yield()
- 실행 중에 우선순위가 동일한 다른 스레드에게 실행 양보
- 자신은 실행 대기 상태로 전환
참고
- https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/lang/Thread.html
- https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/lang/Runnable.html
- 이것이 자바다2 / 신용권 / 한빛미디어
- 자바의 정석 / 남궁성 / 도우출판